Sleep apnea is a common yet serious sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, leading to poor rest quality and potential health risks. If left untreated, sleep apnea can contribute to conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sleep apnea.
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a condition characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep resmed 呼吸機. These interruptions can last from a few seconds to minutes and may occur multiple times per hour. The two main types of sleep apnea are:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): The most common form, caused by throat muscles relaxing excessively, blocking the airway.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): A less common form, where the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing.
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A combination of both OSA and CSA.
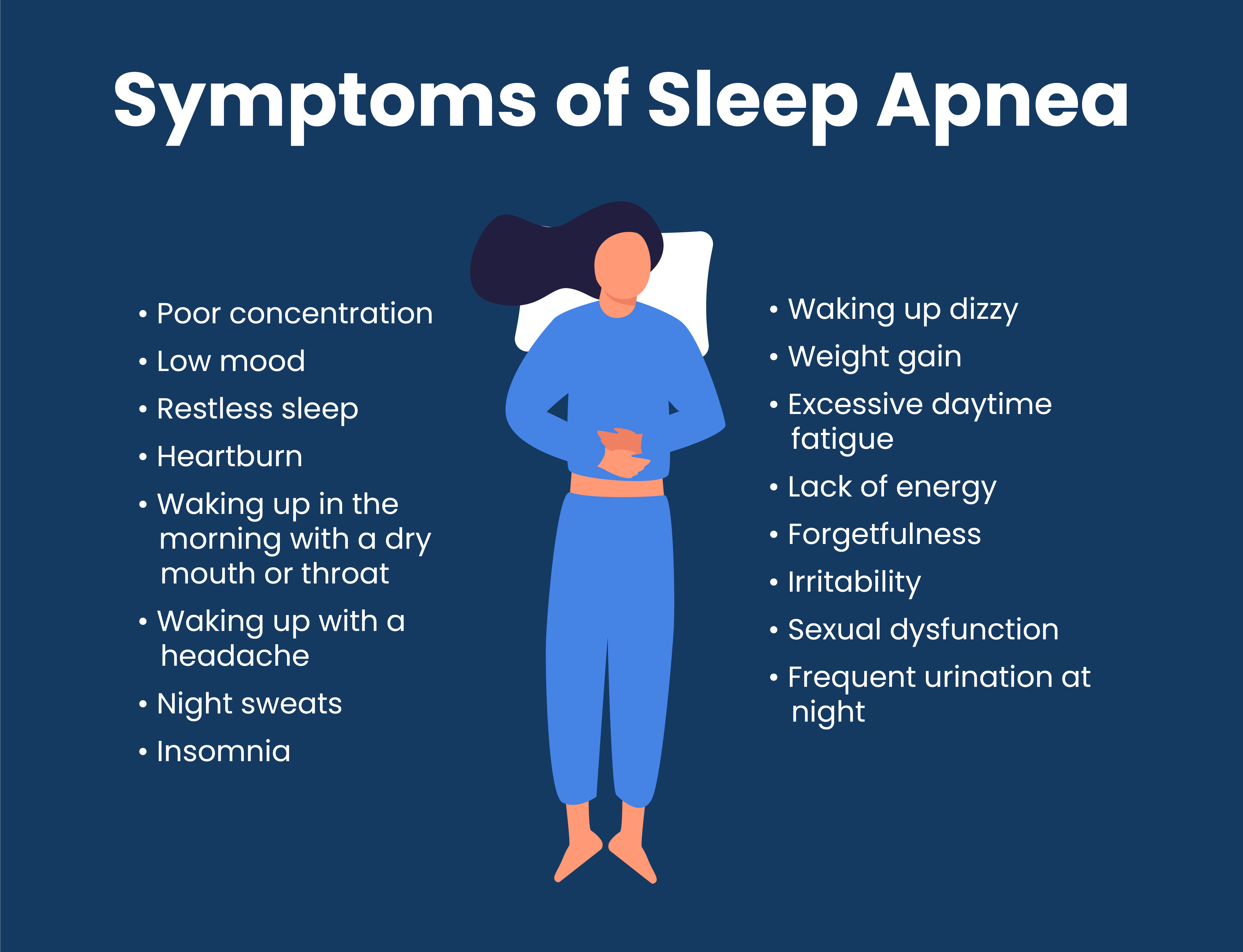
Common Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Recognizing the symptoms of sleep apnea is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Some common signs include:
- Loud snoring
- Episodes of stopped breathing during sleep (noticed by a partner)
- Gasping for air during sleep
- Waking up with a dry mouth or sore throat
- Morning headaches
- Difficulty staying asleep (insomnia)
- Excessive daytime sleepiness (hypersomnia)
- Difficulty concentrating and mood changes
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of sleep apnea:
- Obesity: Excess weight increases fat deposits around the airway, leading to blockages.
- Age: The risk of sleep apnea increases with age.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop sleep apnea than women.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition can increase the likelihood of having sleep apnea.
- Alcohol and Sedative Use: These substances relax the throat muscles, worsening the condition.
- Smoking: Increases inflammation and fluid retention in the airway.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like nasal congestion, heart disorders, and stroke can contribute to sleep apnea.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
If you suspect you have sleep apnea, consult a healthcare professional. Diagnosis usually involves a sleep study (polysomnography) conducted in a sleep center or at home.
Treatment Options
Treatment for sleep apnea varies based on severity:
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss, avoiding alcohol, quitting smoking, and sleeping on one’s side can improve symptoms.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy: The most effective treatment, CPAP involves wearing a mask that delivers continuous air pressure to keep the airway open.
- Oral Appliances: Custom-made devices that adjust the position of the jaw to prevent airway obstruction.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical options like removing excess tissue, repositioning the jaw, or implanting a nerve stimulator may be recommended.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea is a serious health condition that requires attention and treatment. If you or a loved one experience symptoms, seek medical advice to prevent complications and improve quality of life. With the right diagnosis and treatment, sleep apnea can be effectively managed, leading to better sleep and overall health.
